SDS
TITLE:
Drug Design in a rare disease like the Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome: conformational study of the protein EFL1 and the screening of small organic molecules capable of modulating its function
SDS DISEASE
FINANCING SCHEME:
CNCCS Consortium Project “Collezione di Composti Chimici ed attività di screening”
SHORT DESCRIPTION AND USEFUL INFO:
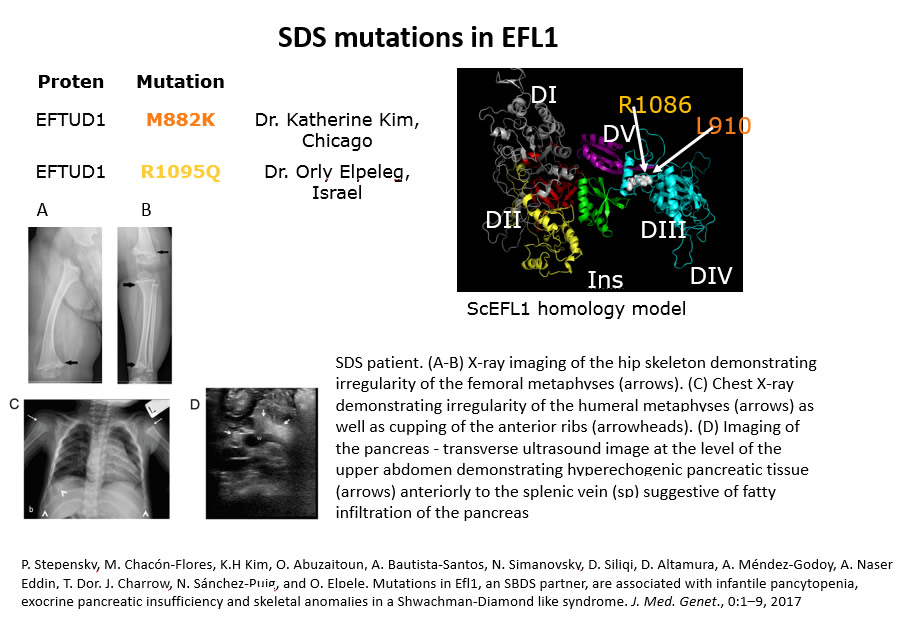
Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome is a very rare genetic disease, for which, currently, there is no cure: in Italy there are 121 patients since 1999. SDS is a complex disease, mainly (about 90% of patients) resulting from the bi-allelic mutation of the SBDS gene (discovered in 2002). The protein encoded by this gene, SBDS, together with the EFL1 protein participate in the cytoplasmic maturation of a ribosomal subunit. Its function is to evict the eIF6 protein (anti-associative factor) from the 60s surface; the latter allows the translation of the competent ribosome. SDS belongs to a class of diseases known as ribosomopathies, related with the alteration of the ribosome structure and / or its biogenesis. Understanding the molecular function of SBDS and EFL1 is not only important for the obvious reason of the medical disease but also because of their relationship to a fundamental biological process such as ribosome assembly and its impact on translation but represents a pathway to understand the role of specialized ribosome to provide regulation and adaptive fitness in an organism.
PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR:
Dott. MICHELE SAVIANO, Dott. DRITAN SILIQI
IC-BARI, via G. Amendola 122/O
70126, Bari
michele.savianoATcnr.it, dritan.siliqiATic.cnr.it
+39 080 5929164